https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001587.htm
Caput succedaneum
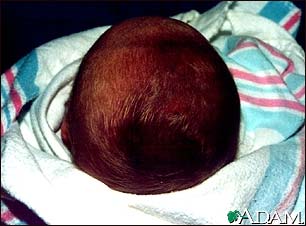
Caput succedaneum is swelling
of the scalp in a newborn. It is most often brought on by pressure from
the uterus or vaginal wall during a head-first (vertex) delivery.
Causes
A
caput succedaneum is more likely to form during a long or hard
delivery. It is more common after the membranes have broken. This is
because the fluid in the amniotic sac is no longer providing a cushion
for the baby's head. Vacuum extraction done during a difficult birth can
also increase the chances of a caput succedaneum.
 A
caput succedaneum may be detected by prenatal ultrasound, even before
labor or delivery begins. It has been found as early as 31 weeks of
pregnancy. Very often, this is due to an early rupture of the membranes
or too little amniotic fluid. It is less likely that a caput will form
if the membranes stay intact.
A
caput succedaneum may be detected by prenatal ultrasound, even before
labor or delivery begins. It has been found as early as 31 weeks of
pregnancy. Very often, this is due to an early rupture of the membranes
or too little amniotic fluid. It is less likely that a caput will form
if the membranes stay intact.
 A
caput succedaneum may be detected by prenatal ultrasound, even before
labor or delivery begins. It has been found as early as 31 weeks of
pregnancy. Very often, this is due to an early rupture of the membranes
or too little amniotic fluid. It is less likely that a caput will form
if the membranes stay intact.
A
caput succedaneum may be detected by prenatal ultrasound, even before
labor or delivery begins. It has been found as early as 31 weeks of
pregnancy. Very often, this is due to an early rupture of the membranes
or too little amniotic fluid. It is less likely that a caput will form
if the membranes stay intact.Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Soft, puffy swelling on the scalp of a newborn infant
- Possible bruising or color change on the scalp swelling area
- Swelling that may extend to both sides of the scalp
- Swelling that is most often seen on the portion of the head which presented first
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will look at the swelling to confirm that it is a caput succedaneum. No other testing is needed.
Treatment
No treatment is needed. The problem most often goes away on its own within a few days.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Complete recovery can be expected. The scalp will go back to a normal shape.
Possible Complications
Complications may include a yellow color to the skin (jaundice) if bruising is involved.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Most
of the time, the problem is noticed right after birth. You do not need
to call your provider unless you have other questions.
Alternative Names
Caput
Images
References
Balest AL, Riley MM, Bogen DL. Neonatology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, eds. Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 2.
Mangurten HH, Puppala BI, Prazad PA. Birth injuries. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 30.
Mangurten HH, Puppala BI, Prazad PA. Birth injuries. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 30.
Review Date 5/14/2017
Updated by: Neil
K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics,
University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed
by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial
Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.










Post a Comment