Blurb:
Phenytoin to treat all seizures but absence
Mech: sodium
Common side effects: rash, nausea, gingival hyperplasia, neuro (ataxia, diplopia, nystagmus)
Serious side effects: hepatotoxicity & myelosuppression
Monitoring: drug-drug (cyp450-hepatotoxicity), drug levels
Mnemonic blurb:
Steers-with-PHUNNY-TOES-IN
For: all seizures but the minor one (absence)
Mech.: Steers
Common side effects: rash (drug-eruption - know this), nausea (all), gingival hyperplasia (kho bo cuoi), neuro (too much phunny)
Serious side effects: injured policeman
Monitoring: injured policeman => drug levels, drug-drug
DRUG NAME
Drug name: PhenytoinMnemonics for name: The steers who walk funny-toes-in (phen-ny-to-in)
Picmonic for name:
|
 |
| The steers with funny-toes-in distract the detonator MECHANISM |
Mnemonics for mechanism: The steers who walk funny-toes-in (phen-ny-to-in) distracts the detonator due to its funny-toes-in appearance. Thus, the detonator cannot explode causing seizures. Note that the detonator is shaped like a salt pepper shaker. The detonator is busy staring at The steers who walk funny-toes-in (phen-ny-to-in) that it does not cause explosives (seizures).
Picmonic for mechinism :
| Salt-containing detonator shaker = causing explosives (seizures) = needs to be distract by the steers that walk Funny-toes-in |
SIDE EFFECTS
Side effects:
Common:
1 - Gingival hyperplasia => unverified but Folic acid may help (3). May need to increase dose for anti-seizure therapeutics (3)
(Mechanism not known, but believed to be multifactorial, and phenytoin pts - not all but it's common for them to get gingival hyperplasia (1) (2)).
Mnemonics for side effects:
- Gingival hyperplasia => think of the steers with funny-toes-in being able to cheat away the salt detonator => the steer is very happy; therefore, it smiles (pho mai con bo cuoi). When it smiles, you realize it has gingival hyperplasia typical of its bovine origin
 |
| Picmonic (product is NOT the cause, used to illustrate only) => Gingival hyperplasia |
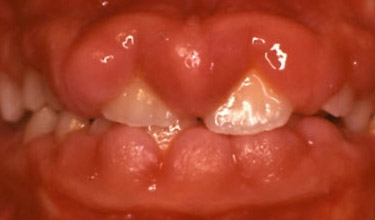 |
| Gingival hyperplasia |
 |
| Gingival hyperplasia |
| Gingival hyperplasia |
Common side effects:
2 - Nausea => mech. unclear but common among many AEDs (4)
Common side effects:
3 - Rash - Morbilliform eruption or "maculopapular drug eruption"
Note: Morbilliform eruption or 'maculopapular drug eruption' is the most common type of drug hypersensitivity reaction. They are characterized by a diffuse and symmetric eruption of erythematous macules or small papules occurring approximately one week after the initiation of drug treatment. In severe forms, the mucosae (oral, conjunctival, nasal, or anogenital) and skin appendages (hair and nails) may be involved." (5)
Treatment & management of rash (6):
"The ultimate goal is always to discontinue the offending medication if possible. Individuals with drug eruptions are often the most ill patients taking the most medications, many of which are essential for their survival. However, all nonessential medications should be limited. Once the offending drug has been identified, it should be promptly discontinued. Knowledge of the common eruption inducing–medications may help in identifying the offending drug.
Patients can possibly continue to be treated through morbilliform eruptions (ie, continue medication even in patients with a rash). The eruption often resolves, especially if the individual is being treated with antihistamines. Most authorities believe that exanthematous drug eruptions are not a precursor to severe reactions, such as TEN. Nevertheless, all patients with severe morbilliform eruptions should be monitored for mucous membrane lesions, blistering, and skin sloughing.
Treatment of a drug eruption depends on the specific type of reaction. Therapy for exanthematous drug eruptions is supportive in nature. First-generation antihistamines are used 24 h/d. Mild topical steroids (eg, hydrocortisone, desonide) and moisturizing lotions are also used, especially during the late desquamative phase.
Severe reactions, such as SJS, TEN, and hypersensitivity reactions, warrant hospital admission. TEN is best managed in a burn unit with special attention given to electrolyte balance and signs of secondary infection. Because adhesions can develop and result in blindness, evaluation by an ophthalmologist is mandatory. In addition, mounting evidence indicates that intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) may improve outcomes for TEN patients.[2, 3, 4]
Hypersensitivity syndrome, a systemic reaction characterized by fever, sore throat, rash, and internal organ involvement, is potentially life threatening. Timely recognition of the syndrome and immediate discontinuation of the anticonvulsant or other offending drug are crucial. Patients may require liver transplantation if the drug is not stopped in time. Treatment with systemic corticosteroids has been advocated."
Common side effects:
4 - Neuro (dose-r/t): nystagmus, diplopia, slurred speech, ataxia
Mechanism: affecting different regions of the brain that caused these side effects such as cerebellar and thus causing ataxia. Also, different Cranial nerves are affected.
It is dose related because when the phenyltoin levels are high, it could cause these side effects. These side effects may go away when the drug is withdrawn.
Mnemonics: The steers with funny-toes-in can cause the people in the geology building which is studying earthquakes and explosions (seizures) to have some funny expressions. These expressions include unable to speak (slurred speech), ataxia (cuoi nga nghieng), eyes going from different side to side (nystagmus & diplopia) and seeing 1-2 people instead of 1.
Serious adverse effects - Toxicity:
1 - Hepatotoxicity => monitor drug levels (after 3-5 half-life); careful evaluation/assessment of drug levels
Mnemonics for Hepatotoxicity from Phenytoin: In order for phenytoin to walk into the geology building disrupting the detonator and making ppl laugh, it had to risk going past the campus policeman by injuring him a bit in order to venture into the geology building where they were testing the detonator.
Serious adverse effects - Toxicity:
Mnemonics to remember: Phenytoin just wanted to disrupt the detonator @ geology building because Phenytoin doesn't believe that it's a good experiment. She doesn't want to cause extra problems with mini smoke bombs (absence seizures).
Also in clinical settings, phenytoin is a drug that needs constant monitoring with its narrow therapeutics index. Therefore, for sth small and minor like absence seizures, it generally is not used.
1 - Hepatotoxicity => monitor drug levels (after 3-5 half-life); careful evaluation/assessment of drug levels
Mnemonics for Hepatotoxicity from Phenytoin: In order for phenytoin to walk into the geology building disrupting the detonator and making ppl laugh, it had to risk going past the campus policeman by injuring him a bit in order to venture into the geology building where they were testing the detonator.
Serious adverse effects - Toxicity:
2 - Myelosuppression => monitor drug levels (after 3-5 half-life's); careful evaluation/assessment of drug levels
PLACE IN THERAPY
All seizures (generalized tonic-clonic & partial seizures) = BUT NOT absence seizures Mnemonics to remember: Phenytoin just wanted to disrupt the detonator @ geology building because Phenytoin doesn't believe that it's a good experiment. She doesn't want to cause extra problems with mini smoke bombs (absence seizures).
Also in clinical settings, phenytoin is a drug that needs constant monitoring with its narrow therapeutics index. Therefore, for sth small and minor like absence seizures, it generally is not used.
References & Resources:
(1) : http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1076264-overview
(2): http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3168966/
(3) interactions btw phenytoin & drugs to counter effects: https://books.google.com/books?id=m0XOBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA225&dq=phenytoin+adverse&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiS7tWRrY_MAhVOwGMKHWYICJAQ6AEIIzAB#v=onepage&q=phenytoin%20adverse&f=false
(4) Pt education resources: https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/8965599/Robinson.html?sequence=2
(5) http://www.uptodate.com/contents/exanthematous-morbilliform-drug-eruption
(6) http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049474-treatment
(5) http://www.uptodate.com/contents/exanthematous-morbilliform-drug-eruption
(6) http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049474-treatment





Post a Comment